Nonlinear Dynamics
The Nonlinear Dynamics of Crime and Criminal Propensity
There are several nonlinear dynamic patterns that seem to provide important clues about the nature of crime and criminal behavior.
Nonlinear Dynamics
The Nonlinear Dynamics of Crime Rates
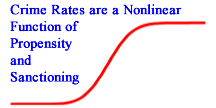
It is proposed that criminal propensity is normally distributed and sanctioning is asymmetric. The interaction between propensity and sanctioning causes a nonlinear sigmoid response in the crime rates when propensity or sanctioning levels change.
The Nonlinear Dynamics of Human Development

It is proposed that there is a five year developmental lag between the nonlinear developmental trajectories of strength and mental capacity. Strength provides the capacity for crime while mental capacity provides control. The interaction between capacity and control over the life-course, in conjunction with the sigmoid nature of crime rates, causes the nonlinear dynamics of the age crime curve.
The Nonlinear Dynamics of Brain Function
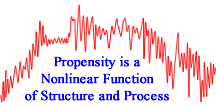
It is proposed that levels of criminal propensity are a function of structure and process in the brain. Over time, the interaction between structure and process produce nonlinear dynamics in the level of criminal propensity over the life-course.
The Nonlinear Dynamics of Sanctioning Efficiency

One of the implications of the nonlinear dynamics of crime rates is that increases in the incarceration level will become rapidly less efficient.